Have you ever wondered about the differences between project management and portfolio management? While they may sound similar, these two disciplines have distinct goals. Project management focuses on the successful completion of individual projects, ensuring that they meet their objectives within the assigned timeline and budget. On the other hand, portfolio management takes a broader perspective by overseeing multiple projects and initiatives, strategically aligning them with organizational goals and optimizing resource allocation. By understanding the unique objectives and approaches of project management and portfolio management, you can better navigate the world of project and portfolio management and achieve greater success in your professional endeavors.
Goal Distinction
In understanding the differences between project management and portfolio management, it is crucial to first consider the distinct goals that each discipline aims to achieve.
Project Management Goals
Project management primarily focuses on the successful completion of a specific project within the defined constraints of time, budget, and quality. The goal of project management is to deliver the desired project outcomes, meet stakeholder expectations, and ensure customer satisfaction. It requires careful planning, execution, and monitoring to ensure that the project objectives are met effectively and efficiently.
Portfolio Management Goals
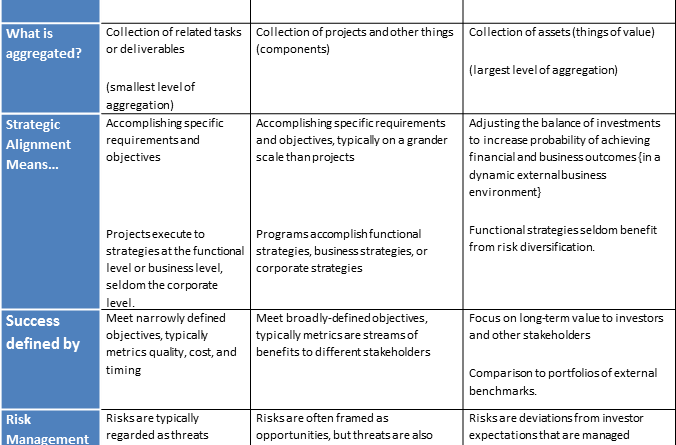
On the other hand, portfolio management takes a more strategic approach towards achieving organizational objectives. The goal of portfolio management is to maximize the value generated by the organization’s portfolio of projects and programs. It involves the selection, prioritization, and optimization of projects and programs to align them with the organization’s overall strategic objectives. The focus is on allocating resources and managing risks across the portfolio to achieve the greatest return on investment.
Scope
The scope of project management and portfolio management also differs significantly. Let’s explore each of them in detail.
Project Management Scope
Project management primarily deals with the execution of individual projects within a specific scope, defined time frame, and allocated resources. It encompasses all the activities required to deliver the project outcomes, such as planning, organizing, executing, controlling, and closing. Project managers are responsible for managing the scope, schedule, budget, risks, and quality of the project to ensure its successful completion.
Portfolio Management Scope
In contrast, portfolio management has a broader scope that extends beyond the boundaries of individual projects. It involves managing a portfolio of projects, programs, and other ongoing initiatives that collectively contribute to the organization’s strategic objectives. Portfolio managers focus on aligning projects and programs with the organization’s strategic goals, evaluating potential investments, and making decisions regarding resource allocation and prioritization. They also monitor and control the performance of the portfolio as a whole to ensure that it delivers the expected value.

Responsibilities
The responsibilities of project management and portfolio management professionals vary based on their respective roles and objectives.
Project Management Responsibilities
Project managers are responsible for the day-to-day management of individual projects. They take charge of planning, executing, monitoring, and controlling all aspects of the project to ensure its successful completion. Their responsibilities include defining the project scope, creating a detailed project plan, allocating resources, managing risks, coordinating team members, tracking progress, and communicating with stakeholders. They are focused on delivering the project on time, within budget, and to the desired quality standards.
Portfolio Management Responsibilities
Portfolio managers, on the other hand, have a more strategic role. Their responsibilities involve overseeing the entire portfolio of projects and programs within an organization. They are responsible for identifying and selecting projects that align with the organization’s strategic objectives, assessing their potential value and risks, allocating resources, monitoring performance, and making decisions regarding project prioritization and termination. Portfolio managers also play a crucial role in stakeholder communication, engaging with senior management, and ensuring that the portfolio delivers the expected benefits and value to the organization.
Time Horizon
Another key distinction between project management and portfolio management lies in the time horizon they operate within.
Project Management Time Horizon
Project management typically operates within a relatively short time frame that spans from the initiation of a project to its completion. The duration of a project can range from a few weeks to several years, depending on its complexity and scale. Project managers are focused on achieving the project objectives, meeting deadlines, and delivering the desired outcomes within the defined time frame.
Portfolio Management Time Horizon
On the other hand, portfolio management takes a longer-term perspective. It considers the entire life cycle of multiple projects, programs, and ongoing initiatives within the portfolio. Portfolio managers analyze the strategic alignment, value, and risks associated with each project or program over time. They make decisions regarding resource allocation, project prioritization, and termination based on the long-term impact on the organization’s strategic objectives. The time horizon for portfolio management can range from a few years to decades, depending on the nature of the organization and its goals.

Hierarchy
The hierarchy of project management and portfolio management within an organization also differs.
Project Management Hierarchy
Project management typically operates at a lower level of the organizational hierarchy. Project managers report to a higher-level manager or executive who oversees multiple projects or programs. They are accountable for the successful delivery of their specific projects, but they do not have direct authority over other projects or the overall organizational strategy.
Portfolio Management Hierarchy
Portfolio management, on the other hand, operates at a higher level of the organizational hierarchy. Portfolio managers often report to senior management or executives who are responsible for the overall strategic direction of the organization. They have the authority to make decisions regarding project selection, prioritization, resource allocation, and overall portfolio performance. Portfolio managers work closely with project managers and other stakeholders to ensure that the portfolio of projects and programs aligns with the organization’s strategic goals.
Focus
The primary focus of project management and portfolio management also differs significantly.
Project Management Focus
Project management focuses on the successful delivery of specific projects within the defined constraints of time, budget, and quality. Project managers are concerned with the day-to-day management of project activities, ensuring that tasks are completed, milestones are met, and objectives are achieved. They emphasize the effective utilization of resources, risk management, and stakeholder communication to ensure project success.
Portfolio Management Focus
Portfolio management, on the other hand, takes a more strategic and holistic approach. It focuses on managing the entire portfolio of projects and programs to maximize overall organizational value. Portfolio managers prioritize projects based on their potential value and strategic alignment, allocate resources effectively, manage risks across the portfolio, and monitor the performance of the portfolio as a whole. They emphasize long-term strategic objectives, benefits realization, and the alignment of projects with the organization’s overall strategy.

Approach
The approach used in project management and portfolio management also varies based on their distinct goals and scopes.
Project Management Approach
Project management follows a more tactical and structured approach. It involves following standardized project management methodologies, such as PRINCE2 or Agile, to plan, execute, and control project activities. Project managers use various tools and techniques to manage scope, schedule, budget, risks, and quality. They focus on delivering specific project outcomes in a controlled and predictable manner, following established project management best practices.
Portfolio Management Approach
In contrast, portfolio management takes a more flexible and adaptive approach. It involves strategic decision-making based on a broader understanding of the organization’s goals, market conditions, and resource availability. Portfolio managers use various frameworks and evaluation techniques to assess project opportunities, analyze risks, and prioritize investments. They continuously monitor the portfolio’s performance and make adjustments as necessary to align with changing business needs and market dynamics.
Metrics and Measurement
The metrics and measures used in project management and portfolio management also differ to evaluate success and performance.
Project Management Metrics
In project management, the success and performance of a project are measured based on predefined metrics such as budget variance, schedule variance, quality metrics, and stakeholder satisfaction. These metrics provide insights into the project’s progress and help project managers identify areas for improvement, ensure adherence to project plans, and drive corrective actions to address any deviations.
Portfolio Management Metrics
In portfolio management, the focus shifts towards broader metrics that measure the overall performance and value generated by the portfolio. Metrics such as return on investment (ROI), net present value (NPV), strategic alignment, risk exposure, and resource utilization are used to assess the portfolio’s performance and its contribution towards achieving the organization’s strategic objectives. These metrics help portfolio managers make informed decisions regarding project selection, resource allocation, and portfolio optimization.

Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder engagement is crucial in both project management and portfolio management, but the nature of stakeholder involvement differs.
Project Management Stakeholder Engagement
Project managers engage with stakeholders who are directly involved in the specific project. They identify project stakeholders, understand their needs and expectations, and involve them in project planning, decision-making, and progress monitoring. Regular communication, collaboration, and feedback gathering are essential to keep stakeholders informed and engaged throughout the project life cycle.
Portfolio Management Stakeholder Engagement
Portfolio managers, on the other hand, engage with a broader range of stakeholders, including senior management, executives, project managers, functional managers, and other key decision-makers. They focus on strategic alignment, benefits realization, and overall portfolio performance. Stakeholder engagement in portfolio management involves frequent communication, negotiation, and collaboration to ensure that the portfolio’s objectives and value proposition are understood and supported by all relevant stakeholders.
Decision-Making Authority
The decision-making authority in project management and portfolio management also varies based on their respective scopes and goals.
Project Management Decision-Making Authority
In project management, decision-making authority primarily lies with the project manager. Project managers have the authority to make decisions regarding project execution, resource allocation, risk management, and scope changes within the defined project boundaries. They collaborate with stakeholders and seek their input, but ultimately, the project manager is responsible for making decisions that drive the project towards successful completion.
Portfolio Management Decision-Making Authority
In contrast, portfolio management involves shared decision-making across multiple stakeholders, with the portfolio manager playing a crucial role. Portfolio managers collaborate with senior management, executives, project managers, and other key stakeholders to make strategic decisions regarding project selection, prioritization, resource allocation, and overall portfolio performance. The decision-making process in portfolio management is based on strategic objectives, market conditions, resource availability, and the potential value and risks associated with each project or program within the portfolio.
In conclusion, while both project management and portfolio management contribute to the successful delivery of organizational objectives, they have distinct goals, scopes, responsibilities, and focus areas. Project management focuses on the successful completion of individual projects, while portfolio management takes a broader strategic approach towards maximizing the value generated by the organization’s portfolio of projects and programs. The hierarchy, time horizon, approach, metrics, stakeholder engagement, and decision-making authority also differ between the two disciplines. Understanding these differences is essential for organizations to effectively utilize project management and portfolio management practices and achieve overall success.







