In this article, you will explore the fascinating relationship between a company’s organizational structure and its impact on project management. By understanding how the design and layout of an organization can shape the success of projects, you will gain valuable insights into enhancing project outcomes. From hierarchies to matrix structures, we will uncover the various ways in which organizational structure affects the planning, coordination, and execution of projects. So, get ready to uncover the secrets behind a company’s organizational structure and its profound influence on project management.
Overview of Organizational Structure
Defining Organizational Structure
Organizational structure refers to the way in which a company is organized and the way in which its employees are structured to fulfill specific roles and responsibilities. It defines how various tasks, workflows, and communication channels are managed within the organization. The organizational structure influences the overall functioning, efficiency, and success of the company’s projects.
Types of Organizational Structures
There are several types of organizational structures commonly used by companies, including functional, project-based, and matrix structures. Each type has its own unique characteristics and impact on project management. Understanding these different structures is essential for project managers to effectively navigate and lead projects within their respective organizational contexts.
Role of Project Management
Understanding Project Management
Project management is the discipline of planning, organizing, and controlling resources to achieve specific project goals and objectives within defined constraints such as time, budget, and scope. It involves the application of various tools, techniques, and skills to successfully execute and deliver projects.
Importance of Project Management
Project management plays a critical role in the success of any project, regardless of the organizational structure. It provides a systematic approach to project execution, ensuring that projects are planned, executed, monitored, and controlled effectively. Project management enables organizations to achieve their strategic objectives by ensuring that projects are delivered on time, within budget, and to the satisfaction of stakeholders.
Link between Organizational Structure and Project Management
Alignment of Project Objectives
Organizational structure directly influences how project objectives are aligned with the overall goals and objectives of the company. In a functional structure, project objectives may need to be aligned with the goals of specific departments, while in project-based or matrix structures, project objectives are usually aligned with the strategic objectives of the organization as a whole. The alignment of project objectives ensures that projects contribute to the overall success and growth of the company.
Communication and Decision-Making
The organizational structure significantly impacts communication and decision-making within the company and, consequently, project management. In a functional structure, communication and decision-making are typically hierarchical and department-focused. In project-based or matrix structures, communication is often more cross-functional and collaborative, leading to more effective decision-making. Project managers must understand and adapt to the specific communication and decision-making processes within their organizational structures to ensure efficient project management.
Authority and Reporting Lines
Authority and reporting lines are strongly influenced by organizational structure. In a functional structure, project managers often have limited decision-making authority and report to functional managers. In project-based or matrix structures, project managers may have more authority and report directly to higher-level management or project sponsors. The clarity of authority and reporting lines is crucial for effective project management, as it determines the project manager’s ability to make decisions, allocate resources, and ensure project success.
Resource Allocation and Flexibility
Organizational structure also affects resource allocation and flexibility in project management. In a functional structure, resources may be allocated based on departmental priorities, which can lead to resource limitations and conflicts among projects. In project-based or matrix structures, resources can be allocated more flexibly, allowing for better resource utilization and coordination across projects. Project managers must navigate the resource allocation processes within their organizational structures to ensure that projects have the necessary resources to be successful.
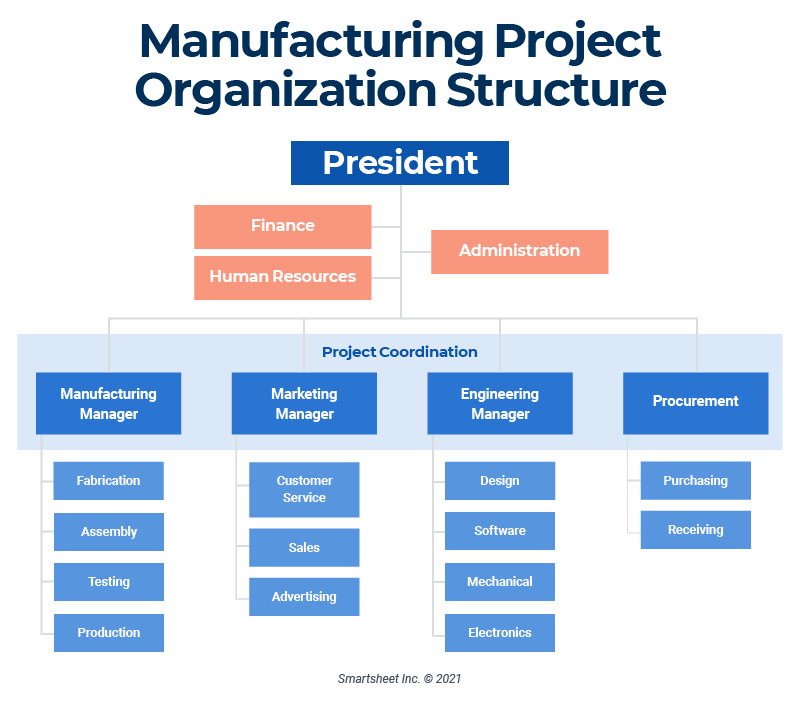
Functional Organizational Structure
Definition and Characteristics
A functional organizational structure groups employees based on their specific functions or areas of expertise. Each department or functional area is responsible for specific tasks, and employees report to a functional manager who oversees their work. This structure promotes specialized knowledge and expertise within each department, allowing for efficient functional operations.
Pros and Cons
The functional organizational structure has several advantages. It encourages deep expertise and specialization within functional areas, fosters efficient communication and decision-making within departments, and provides clear career paths and development opportunities for employees. However, it can also lead to siloed thinking, limited cross-functional collaboration, and challenges in managing projects that require coordination across multiple departments.
Impact on Project Management
In a functional organizational structure, project managers often have limited authority and need to rely on functional managers for resources and decision-making. This can create challenges in coordinating and prioritizing projects, as the departmental priorities may not align with the project objectives. Project managers must effectively communicate and collaborate with functional managers to ensure that projects are successfully executed within the constraints of the organizational structure.
Project-Based Organizational Structure
Definition and Characteristics
A project-based organizational structure is designed around projects rather than functional areas. Employees are organized into project teams, and each team is responsible for the execution of a specific project. The project manager has direct control over the project team, including resource allocation, decision-making, and coordination.
Pros and Cons
The project-based organizational structure offers several benefits. It promotes cross-functional collaboration, allows for efficient communication and decision-making within project teams, and enables flexibility and adaptability to changing project requirements. However, it can also create challenges in resource allocation, as employees may be dedicated to specific projects, leading to potential resource limitations for other projects within the organization.
Impact on Project Management
In a project-based organizational structure, project managers have direct authority over resources and decision-making, enabling them to have better control and coordination over projects. This structure facilitates effective communication and collaboration within project teams, fostering a sense of shared purpose and commitment. However, project managers may need to navigate resource constraints and potential conflicts among projects to ensure their successful delivery.
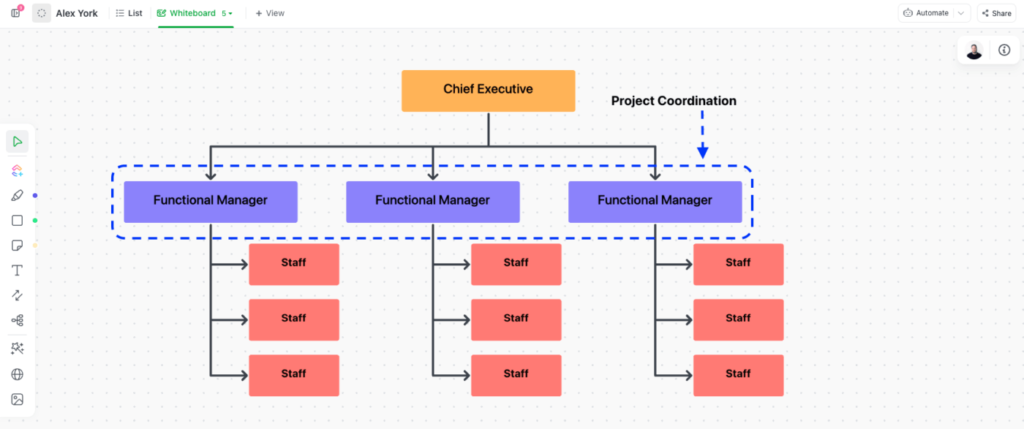
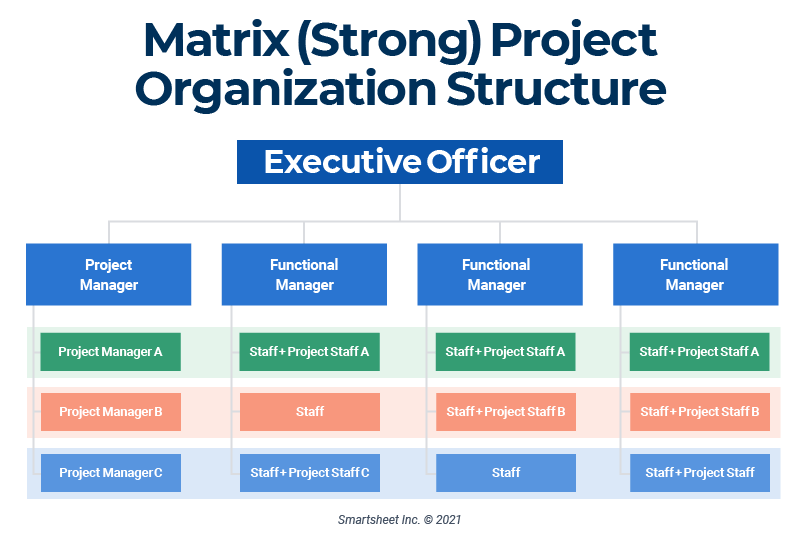
Matrix Organizational Structure
Definition and Characteristics
A matrix organizational structure is a hybrid structure that combines aspects of both functional and project-based structures. Employees usually have dual reporting lines: one to a functional manager and another to a project manager. This allows for the simultaneous focus on specific functional tasks and the successful execution of projects.
Pros and Cons
The matrix organizational structure offers several advantages. It promotes both functional expertise and project execution, encourages cross-functional collaboration, and facilitates effective resource utilization. However, it can also create challenges in managing dual reporting lines, potential conflicts between functional and project goals, and complexity in decision-making processes.
Impact on Project Management
In a matrix organizational structure, project managers have the authority to manage the project team, while functional managers are responsible for the employees’ functional aspects. This structure requires effective communication, collaboration, and negotiation between project managers and functional managers to ensure that projects are successfully executed while maintaining the efficiency of functional operations. Project managers must navigate the complexities of dual reporting lines and ensure that both functional and project goals are aligned.
Organizational Culture
Definition and Influence
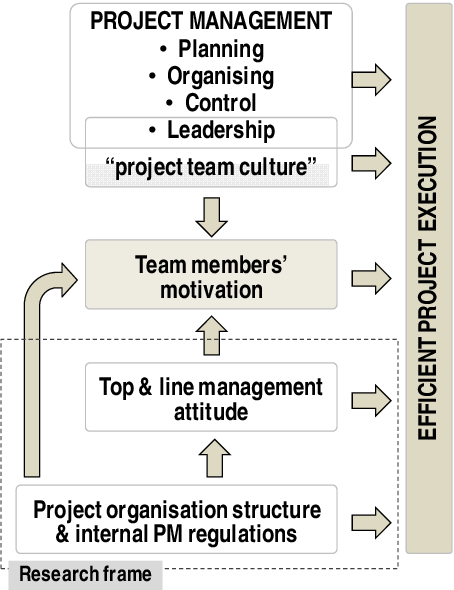
Organizational culture refers to the shared values, beliefs, and norms that shape the behavior, attitudes, and interactions of employees within an organization. It influences how employees perceive and approach their work, make decisions, and collaborate with others. Organizational culture plays a significant role in project management, as it influences the project team’s dynamics, motivation, and commitment to project goals.
Culture and Project Management
Organizational culture can either support or hinder effective project management. A culture that values teamwork, collaboration, and innovation fosters an environment conducive to successful project execution. On the other hand, a culture that promotes individualism, resistance to change, or rigid hierarchy may create challenges in project management. Project managers must understand and work within the organizational culture to ensure that projects are executed in a manner aligned with the cultural values of the company.
Leadership Style
Impact of Leadership on Project Management
Leadership style has a significant impact on project management outcomes. The leadership style adopted by the project manager influences team dynamics, motivation, and decision-making processes. Effective leadership fosters collaboration, provides clear direction and guidance, and empowers team members to contribute their best to the project’s success.
Leadership Styles and Organizational Structures
Different leadership styles may be more suitable for specific organizational structures. For example, a functional structure may benefit from a directive or autocratic leadership style to ensure efficient operations within departments. A project-based or matrix structure may require a more participative or democratic leadership style to foster collaboration and engagement across project teams. Project managers must adapt their leadership styles to align with the organizational structure and the needs of the project.
Challenges in Managing Projects within Organizational Structures
Conflicting Priorities and Resources
Managing projects within organizational structures often involves dealing with conflicting priorities and limited resources. Functional structures may prioritize departmental goals over project objectives, leading to resource limitations for projects. Project-based or matrix structures may face challenges in resource allocation, as employees may be dedicated to specific projects, leading to potential shortages for other projects. Project managers need to effectively communicate, negotiate, and align priorities to overcome these challenges.
Lack of Cross-Functional Collaboration
In some organizational structures, there may be a lack of cross-functional collaboration, which can hinder effective project management. Siloed thinking, departmental rivalries, or communication barriers may prevent project teams from leveraging the expertise and resources available across the organization. Project managers must foster a culture of collaboration, establish effective communication channels, and promote knowledge sharing to overcome these barriers and ensure successful project execution.
Communication Barriers
Communication barriers can arise in any organizational structure and pose challenges to project management. In a functional structure, communication may be hierarchical and limited to specific departments, making it difficult to disseminate information or coordinate across projects. In project-based or matrix structures, communication may become complex due to multiple reporting lines and cross-functional teams. Project managers must actively address communication barriers, promote transparent communication channels, and ensure that information flows efficiently across stakeholders and project teams.
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common challenge in managing projects within organizational structures. The disruption caused by projects may be perceived as a threat to established routines, power dynamics, or job security, leading to resistance from employees or stakeholders. Project managers must anticipate and address resistance to change through effective change management strategies, clear communication of project benefits, and active involvement and engagement of key stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle.
Best Practices for Effective Project Management
Adapting the Organizational Structure to Project Needs
One of the key best practices for effective project management is to adapt the organizational structure to the specific needs of the project. This may involve creating project teams or temporarily modifying reporting lines within the existing structure to foster collaboration and resource allocation. By aligning the organizational structure with the project requirements, project managers can optimize project execution and enhance the chances of project success.
Effective Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are crucial for effective project management. Project managers must establish clear lines of communication, promote transparency, and encourage open and frequent communication among project team members and stakeholders. Collaboration tools and platforms can facilitate efficient information sharing, decision-making, and coordination. By fostering effective communication and collaboration, project managers can enhance project outcomes and mitigate potential risks.
Empowering Project Managers
Empowering project managers is essential for driving successful project management. Project managers should be given the necessary authority, autonomy, and decision-making power to effectively manage project resources, make critical decisions, and drive project success. Empowerment enables project managers to take ownership, inspire and motivate their teams, and overcome challenges within the organizational structure.
Continuous Learning and Improvement
Continuous learning and improvement are critical for effective project management. Project managers should actively seek feedback, evaluate project outcomes, and identify areas for improvement. Lessons learned from previous projects should be documented and shared within the organization to enhance project management practices. By promoting a culture of continuous learning and improvement, project managers can drive innovation, efficiency, and success in managing projects within their respective organizational structures.
In conclusion, a company’s organizational structure significantly impacts project management. The type of structure, whether functional, project-based, or matrix, influences how projects are aligned with organizational objectives, the communication and decision-making processes, resource allocation, and flexibility. Organizational culture and leadership style also play crucial roles in project management outcomes. Despite the challenges that may arise, adapting the organizational structure to project needs, fostering effective communication and collaboration, empowering project managers, and promoting a culture of continuous learning and improvement are key best practices for successful project management within any organizational structure.