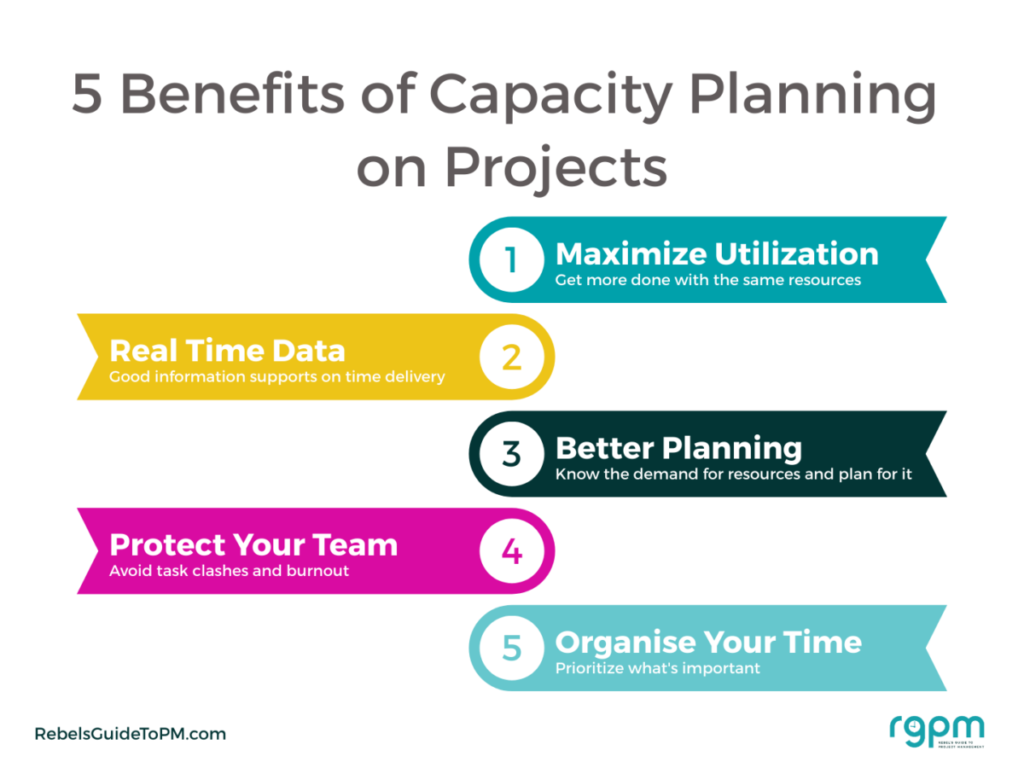
Are you curious about the concept of capacity in project management? If so, you’re in the right place! This article aims to provide a clear understanding of what capacity means in the context of project management. Whether you are new to this field or seeking to enhance your knowledge, exploring the concept of capacity will help you effectively plan and execute projects. So, let’s dive into the world of capacity and uncover its significance in project management!
What is Capacity in Project Management
Definition of capacity in project management
Capacity in project management refers to the maximum amount of work that a team or organization can accomplish within a specific timeframe. It is the measure of an entity’s ability to effectively utilize its available resources, such as people, equipment, and materials, to complete tasks and deliver the desired project outcomes. In simpler terms, capacity represents the limit of how much work can be done by a team or an organization.
Importance of understanding capacity in project management
Understanding and managing capacity is crucial in project management as it directly impacts the success of a project. By effectively utilizing resources and ensuring that the workload is balanced, project managers can improve efficiency, productivity, and ultimately, project outcomes. Proper capacity planning allows for better allocation of resources, identification of constraints, and mitigation of risks, enabling projects to stay on track and meet deadlines.
Factors affecting capacity in project management
Several factors can influence capacity in project management. These include:
-
Resource availability: The availability of skilled personnel, equipment, and materials directly affects the capacity to undertake and complete tasks within a given time frame. Insufficient resources can lead to delays and potentially compromise project success.
-
Skillset and expertise: The skills and expertise possessed by team members play a significant role in determining capacity. A highly skilled team can accomplish more tasks efficiently, thereby increasing overall capacity.
-
External dependencies: Projects often rely on external factors that are beyond the project team’s control, such as suppliers, vendors, or regulatory agencies. Delays or issues with these dependencies can impact capacity.
-
Project complexity and scope: More complex projects with larger scopes require greater capacity to successfully execute. Understanding the complexity and scope of a project is essential in determining the required capacity.
-
Time constraints: The project timeline and deadlines set specific time constraints on the capacity available. Projects with strict time constraints may require additional resources or a more efficient use of existing resources.
By considering these factors and adapting capacity planning accordingly, project managers can better anticipate potential challenges and make informed decisions to optimize capacity utilization.
Planning for Capacity
Understanding project requirements
To effectively plan for capacity, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the project requirements. Project managers should thoroughly analyze the project scope, objectives, and deliverables to determine the specific activities and tasks that need to be completed. By having a detailed understanding of the project requirements, project managers can accurately identify the necessary resources and allocate them efficiently.
Identifying available resources
The next step in capacity planning is to identify the resources available for the project. This includes both human resources and material resources. Project managers should assess the skills, expertise, and availability of team members and consider any constraints or limitations on the availability of equipment or materials. By understanding the resources already at hand, project managers can assess the existing capacity and identify any potential gaps or areas needing improvement.
Assessing resource capabilities
Once the available resources have been identified, project managers need to assess the capabilities of each resource. This involves evaluating the skill sets, experience, and knowledge of individual team members, as well as considering their workload and availability. Understanding the capabilities of each resource enables project managers to allocate tasks and responsibilities effectively, ensuring that the right people are assigned to the right tasks. This assessment also helps in identifying any training needs or areas where additional resources may need to be recruited or outsourced.

Estimating Capacity
Methods for estimating capacity
Estimating capacity involves predicting the maximum work that can be accomplished within a given timeframe. There are several methods project managers can use to estimate capacity, including:
-
Historical data analysis: By analyzing past project data, project managers can identify patterns and trends in resource utilization and project outcomes. This allows for more accurate estimation of capacity based on historical performance.
-
Expert judgment: Project managers can leverage the expertise of senior team members or consultants who have experience in similar projects. This approach involves seeking opinions and insights from those who have a deep understanding of the domain or industry to estimate capacity.
-
Parametric estimation: Parametric estimation involves using mathematical models and statistical techniques to estimate capacity based on specific parameters, such as the number of resources, their productivity rates, and the complexity of tasks.
-
Bottom-up estimation: This approach involves breaking down the project into smaller tasks and estimating the capacity required for each task. The individual estimates are then aggregated to determine the overall project capacity.
Factors to consider in capacity estimation
When estimating capacity, there are several factors that project managers need to consider:
-
Task dependencies: The interdependencies between tasks can impact capacity estimation. Tasks that are dependent on the completion of other tasks may require additional capacity to account for potential delays or issues.
-
Contingencies: Project managers should include contingencies in their capacity estimates to allow for unexpected events or changes. This provides a buffer for any unforeseen circumstances that may affect capacity.
-
Learning curve: If the project involves new technologies or processes, there may be a learning curve for the team members. Project managers should consider the additional time needed to acquire and apply new skills when estimating capacity.
-
Resource availability: The availability of resources, including internal team members and external contractors, should be taken into account during capacity estimation. Project managers should consider any constraints or limitations that may impact the availability of resources.
-
Project constraints: Projects often have specific constraints, such as budget limitations or regulatory requirements. These constraints may impact capacity and should be considered during estimation.
By considering these factors and utilizing appropriate estimation methods, project managers can develop accurate capacity estimates that align with project requirements.
Estimating capacity for different project phases
Capacity estimation should be conducted for different project phases to ensure that resources are allocated appropriately throughout the project lifecycle. Project phases, such as initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closing, may require different levels of capacity and resource allocation.
During the initial project phases, such as initiation and planning, capacity estimation helps in determining the overall level of effort required to complete the project successfully. It allows project managers to allocate resources for tasks such as defining scope, analyzing risks, and establishing project schedules.
As the project progresses into the execution phase, capacity estimation helps in allocating resources for specific tasks and tracking resource utilization. It enables project managers to identify any capacity constraints or issues early on and take necessary actions to resolve them.
In the monitoring and control phase, ongoing capacity estimation helps project managers track the progress of tasks and make adjustments as needed. It allows for reallocation of resources based on the changing project needs, ensuring that capacity is optimized.
Finally, during the project closing phase, capacity estimation helps in evaluating the utilization of resources and identifying any lessons learned for future projects. It provides insights into the effectiveness of the capacity planning process and helps to improve future capacity estimations.
By estimating capacity for different project phases, project managers can better manage resources, adapt to changing requirements, and maximize the overall project efficiency.
Managing Capacity Constraints
Recognizing capacity constraints
Capacity constraints are situations where the available resources are insufficient to meet the demands of a project. It is important for project managers to recognize these constraints early on to avoid potential delays, cost overrun, or compromised project outcomes. Some common signs of capacity constraints include missed deadlines, increased workload for team members, and low productivity levels.
To recognize capacity constraints, project managers should regularly review resource utilization, monitor the progress of tasks, and engage in open communication with team members. By keeping a close eye on resource allocation and team performance, project managers can identify signs of capacity constraints and take proactive measures to address them.
Strategies for alleviating capacity constraints
When capacity constraints are identified, project managers can implement various strategies to alleviate them and ensure that projects stay on track. Some key strategies include:
-
Resource leveling: Resource leveling involves adjusting the project schedule or reallocating resources to balance the workload across the team. By avoiding resource overloads and ensuring a more equitable distribution of tasks, capacity constraints can be alleviated.
-
Resource optimization: Project managers should identify opportunities to optimize resource utilization by matching the skills and expertise of team members to the tasks at hand. This allows for the efficient allocation of resources and maximizes their productivity, reducing capacity constraints.
-
Outsourcing or external resourcing: In situations where internal resources are insufficient, project managers can consider outsourcing certain tasks or bringing in external resources. This allows for the temporary augmentation of capacity to meet project demands.
-
Training and skill development: If capacity constraints are due to a lack of skills or knowledge, project managers should invest in training and skill development programs for team members. By enhancing the skills of the existing workforce, capacity constraints can be mitigated in the long run.
-
Prioritization and trade-offs: When faced with capacity constraints, project managers may need to prioritize tasks, reevaluate project scope, or negotiate with stakeholders to make trade-offs. These actions can help manage capacity constraints within the available resources and time frame.
Mitigating risks associated with capacity constraints
Capacity constraints can introduce risks to project success, such as delays, increased costs, or compromised quality. To mitigate these risks, project managers should:
-
Identify potential risks: Project managers should identify the risks associated with capacity constraints early on. This includes analyzing the impact of constraints on project objectives, deadlines, and overall project performance.
-
Develop contingency plans: Contingency plans should be developed to address potential risks and mitigate the impact of capacity constraints. These plans may involve reallocating resources, adjusting project schedules, or seeking additional resources to alleviate constraints.
-
Regularly monitor and assess risks: It is crucial to continuously monitor and assess risks throughout the project lifecycle. By staying vigilant and regularly reviewing the impact of capacity constraints, project managers can identify emerging risks and take proactive measures to mitigate them.
-
Foster open communication: Building a culture of open communication and collaboration within the project team is vital in managing capacity constraints. When team members feel comfortable reporting issues or constraints, it facilitates early identification and timely resolution of risks.
By implementing appropriate strategies and actively managing the risks associated with capacity constraints, project managers can ensure that projects stay on track and achieve desired outcomes.
Optimizing Capacity Utilization
Maximizing efficiency through resource allocation
Optimizing capacity utilization involves maximizing the efficiency and productivity of available resources. One key aspect of achieving this optimization is through effective resource allocation. By ensuring that the right resources are assigned to the right tasks, project managers can enhance productivity, reduce bottlenecks, and make the most efficient use of available capacity.
To maximize efficiency through resource allocation, project managers should consider the following best practices:
-
Match skills and expertise: Assigning tasks to team members who possess the required skills and expertise ensures that the work is performed efficiently and effectively. By leveraging the specific strengths of each individual, project managers can optimize the overall capacity utilization.
-
Consider workload balance: Balancing the workload across the team helps in avoiding resource overloads and ensures that no team member is overwhelmed with an excessive amount of work. By distributing tasks evenly, project managers can optimize capacity utilization and reduce the risk of burnout or decreased performance.
-
Utilize tools and software: Project management software and tools can greatly aid in optimizing resource allocation and capacity utilization. These tools provide visibility into resource availability, workload distribution, and task dependencies, enabling project managers to make informed decisions and maximize efficiency.
-
Regularly review and adjust allocation: Resource allocation should be regularly reviewed and adjusted as needed throughout the project lifecycle. By monitoring resource utilization, project managers can identify inefficiencies or imbalances and take necessary actions to optimize capacity utilization.
By effectively allocating resources based on skills, workload balance, and utilizing the right tools, project managers can optimize capacity utilization and improve project efficiency.
Balancing workloads across the team
Balancing workloads across the project team is crucial in optimizing capacity utilization. It involves distributing tasks in a way that evenly distributes the workload and prevents resource overloads or underutilization. By achieving a balanced workload, project managers can ensure that resources are utilized optimally, leading to enhanced productivity and reduced capacity constraints.
To balance workloads effectively, project managers should:
-
Understand individual capabilities: Project managers should have a clear understanding of each team member’s capabilities, skills, and expertise. By aligning tasks with the right individuals, project managers can avoid overloading or underutilizing resources.
-
Consider individual workload capacity: Each team member has a finite capacity or limit to the amount of work they can effectively handle. Project managers should assess individual workload capacities and distribute tasks accordingly, keeping in mind the skill sets, expertise, and availability of team members.
-
Evaluate task complexity: Some tasks may require more time or effort than others due to their complexity. Project managers should consider the complexity of tasks when assigning them, ensuring that the workload is balanced across the team.
-
Foster collaboration and teamwork: Encouraging collaboration and teamwork within the project team fosters a supportive environment where team members can rely on each other and seek assistance when needed. This helps in balancing workloads by enabling team members to share tasks and support each other during peak workload periods.
By actively balancing workloads and ensuring that tasks are distributed equitably, project managers can optimize capacity utilization and enhance overall project efficiency.
Optimizing capacity planning for multiple projects
In organizations where multiple projects are being concurrently executed, optimizing capacity planning becomes critical. It is essential to ensure that resources are effectively allocated across multiple projects to avoid overload, prevent bottlenecks, and optimize capacity utilization.
To optimize capacity planning for multiple projects, project managers should consider the following strategies:
-
Prioritize projects: Prioritize projects based on their strategic importance, alignment with organizational goals, and resources required. By focusing on high-priority projects, project managers can allocate resources more effectively and maximize overall capacity utilization.
-
Resource sharing and collaboration: Encourage resource sharing and collaboration between projects. By creating a culture of teamwork and collaboration, project managers can leverage the expertise and skills of individuals across different projects. This allows for better resource utilization and increased capacity.
-
Regularly assess resource availability: Continuously assess the availability of resources across multiple projects. This involves monitoring resource utilization, forecasting future demands, and making informed decisions on resource allocation and balancing workload.
-
Utilize resource management tools: Resource management tools can greatly assist in optimizing capacity planning for multiple projects. These tools provide visibility into resource availability, allow for resource bookings and allocations, and enable project managers to identify any potential conflicts or mismatches in resource allocation.
By proactively managing resource allocation, fostering collaboration between projects, regularly assessing resource availability, and leveraging resource management tools, project managers can optimize capacity planning for multiple projects and improve overall project success.
Tracking and Monitoring Capacity
Implementing performance metrics
Tracking and monitoring capacity requires the implementation of performance metrics that provide insights into resource utilization, project progress, and overall capacity utilization. These metrics allow project managers to assess the effectiveness of capacity planning and make data-driven decisions to optimize capacity utilization.
Some key performance metrics for tracking and monitoring capacity include:
-
Resource utilization rate: This metric measures the percentage of time that resources are actively engaged in project work. It provides insights into resource availability and helps project managers identify any underutilized or overloaded resources.
-
Task completion rate: Task completion rate measures the efficiency and progress of individual tasks. By tracking task completion rates, project managers can identify potential bottlenecks or areas where capacity constraints may exist.
-
Schedule adherence: Schedule adherence assesses the degree to which project activities are completed within the planned timeframe. By monitoring schedule adherence, project managers can identify any delays or issues that may indicate capacity constraints.
-
Workload balance: This metric measures the balance of workload across the team. It evaluates the distribution of tasks and assesses whether the workload is evenly distributed, ensuring that no team member is overloaded or underutilized.
Implementing these performance metrics allows project managers to track resource utilization, project progress, and overall capacity utilization. By regularly reviewing and analyzing these metrics, project managers can identify any areas needing improvement and make necessary adjustments to optimize capacity utilization.
Regularly reviewing and updating capacity plans
Capacity planning is an ongoing process that requires regular reviews and updates. As projects evolve and requirements change, capacity plans should be adjusted to ensure that resources are effectively allocated and capacity constraints are addressed.
Regularly reviewing and updating capacity plans involves:
-
Periodic capacity reviews: Project managers should conduct periodic reviews of capacity plans to assess their effectiveness. These reviews should consider feedback from team members, performance metrics, and any changes in project requirements or constraints. By identifying any gaps or areas where capacity needs adjustment, project managers can make timely updates to optimize resource allocation.
-
Scenario planning: Project managers should engage in scenario planning to anticipate potential changes or risks that may impact capacity. By considering different scenarios and their potential effects on capacity, project managers can develop contingency plans and be better prepared to address any capacity constraints that may arise.
-
Stakeholder engagement: It is important to engage with stakeholders throughout the capacity planning process. Regular communication and collaboration with stakeholders help project managers understand changing requirements, provide updates on resource availability, and make necessary adjustments to capacity plans.
By regularly reviewing and updating capacity plans, project managers can ensure that resources are effectively allocated, capacity constraints are addressed, and projects stay on track.
Effective communication and collaboration in capacity tracking
Effective communication and collaboration are key elements in tracking and monitoring capacity. Project managers should establish clear channels of communication and foster collaboration within the project team to ensure that capacity constraints can be identified and addressed in a timely manner.
To facilitate effective communication and collaboration in capacity tracking, project managers should:
-
Establish regular check-ins: Regular check-ins with team members provide an opportunity to discuss project progress, resource utilization, and any potential capacity constraints. These check-ins promote open communication and help project managers identify any issues or concerns related to capacity.
-
Encourage feedback and suggestions: Project managers should encourage team members to provide feedback and suggestions regarding capacity. By creating a culture where team members feel comfortable expressing concerns or proposing solutions, project managers can gain valuable insights into potential capacity constraints and make necessary adjustments.
-
Collaborative decision-making: When it comes to resource allocation and capacity planning, involving the project team in the decision-making process can lead to better outcomes. By considering the input and perspectives of team members, project managers can optimize capacity utilization and enhance overall project success.
-
Transparency and visibility: Providing transparency and visibility into capacity planning and tracking helps team members understand the rationale behind resource allocations and enables them to align their efforts accordingly. This transparency fosters trust and collaboration among team members.
By fostering effective communication and collaboration, project managers can create a supportive environment where capacity constraints can be identified early on and addressed collaboratively, leading to improved project outcomes.
Capacity and Risk Management
Understanding the relationship between capacity and risk
Capacity and risk management are closely intertwined in the context of project management. Capacity constraints can introduce risks to project success, such as delays, increased costs, or compromised project outcomes. On the other hand, effective capacity management can help mitigate risks and ensure that projects stay on track.
Understanding the relationship between capacity and risk involves:
-
Identifying capacity-related risks: Project managers should identify potential risks arising from capacity constraints. These risks may include delays in task completion, overworked team members, decreased productivity, or compromised quality. By recognizing these risks, project managers can develop strategies to mitigate their impact.
-
Assessing the impact of capacity constraints: When capacity constraints occur, project managers need to assess their impact on project objectives, deadlines, and overall project performance. This assessment allows project managers to understand the potential risks associated with capacity constraints and make informed decisions to manage them.
-
Balancing risk and capacity: Managing capacity involves finding a balance between optimizing capacity utilization and mitigating risks. Project managers need to assess the capacity requirements of the project while considering the associated risks. This involves making trade-offs and prioritizing actions to manage both capacity constraints and associated risks effectively.
By understanding the relationship between capacity and risk, project managers can proactively manage both aspects to ensure project success.
Addressing risks associated with capacity constraints
Capacity constraints can introduce various risks to project success. To address these risks, project managers can implement several strategies:
-
Developing contingency plans: Contingency plans should be developed to address potential risks associated with capacity constraints. These plans involve having alternate approaches, resources, or schedules in place to mitigate the impact of capacity constraints.
-
Prioritizing critical tasks: Project managers should identify critical tasks that are essential to project success and prioritize their completion. By focusing on these critical tasks, project managers can reduce the impact of capacity constraints on project outcomes.
-
Seeking additional resources: If capacity constraints persist despite mitigation efforts, project managers should consider seeking additional resources. This may involve outsourcing certain tasks or temporarily bringing in external resources to alleviate capacity constraints and reduce associated risks.
-
Adjusting project schedules: When capacity constraints arise, project managers can consider adjusting project schedules to accommodate additional resources or create buffer time. This allows for a more realistic timeline and reduces the risk of delays due to capacity constraints.
By implementing these strategies, project managers can address the risks associated with capacity constraints and ensure that project outcomes are not compromised.
Mitigating risks through proactive capacity management
Proactive capacity management is essential for mitigating risks associated with capacity constraints. By anticipating potential challenges, project managers can make informed decisions and take necessary actions to mitigate risks and ensure project success.
To mitigate risks through proactive capacity management, project managers should:
-
Conduct regular capacity assessments: Regularly assessing the capacity requirements of the project helps project managers identify any potential capacity constraints. By conducting these assessments throughout the project lifecycle, project managers can proactively manage risks associated with capacity constraints.
-
Continuously monitor resource utilization: Monitoring resource utilization allows project managers to identify any inefficiencies or imbalances that may indicate potential risks. By staying vigilant and regularly reviewing resource utilization, project managers can take timely actions to mitigate risks.
-
Iterate and adjust capacity plans: Capacity plans should be flexible and adaptable. As project requirements or constraints change, project managers should iterate and adjust capacity plans accordingly. This agile approach allows for better risk mitigation and ensures that capacity constraints are addressed proactively.
-
Foster a culture of risk management: Project managers should foster a culture of risk management within the project team. Encouraging team members to be proactive in identifying and addressing risks associated with capacity constraints contributes to a collective effort in risk mitigation.
By adopting a proactive approach to capacity management and actively mitigating risks associated with capacity constraints, project managers can improve project success rates and ensure that project outcomes are not compromised.
Adapting Capacity for Changing Situations
Flexibility in capacity planning
Flexibility is essential in capacity planning to adapt to changing situations. Project managers should anticipate that project requirements, resource availability, and constraints may change throughout the project lifecycle. Having a flexible capacity planning approach allows for swift adjustments and ensures that resources are effectively allocated despite changing circumstances.
To incorporate flexibility into capacity planning, project managers should:
-
Maintain regular communication: Regular and open communication with stakeholders, team members, and other relevant parties is crucial. This communication helps project managers stay informed about any changes in project requirements, resource availability, or constraints, enabling them to adapt capacity plans accordingly.
-
Continuously evaluate resource requirements: Resource requirements may change as the project progresses. Project managers should regularly evaluate resource needs and make adjustments to capacity plans as necessary. This may involve adding or reallocating resources to address changing requirements.
-
Plan for contingencies: Contingency planning should be an integral part of capacity planning to address potential changes or risks. Project managers should have backup plans and alternative approaches in place, allowing for quick adaptation and resource reallocation when unexpected situations arise.
-
Monitor and assess performance: Monitoring and assessing the performance of resources and tasks is key to identifying any deviations from the planned capacity. By regularly reviewing performance metrics and identifying areas that require adjustment, project managers can proactively adapt capacity plans.
By incorporating flexibility into capacity planning, project managers can effectively adapt to changing situations and ensure that resources are optimally allocated despite evolving project requirements or constraints.
Managing capacity changes due to unforeseen circumstances
Unforeseen circumstances can significantly impact capacity in project management. Unexpected events such as resource unavailability, equipment breakdowns, or external dependencies can disrupt planned capacity and affect project outcomes. To manage capacity changes due to unforeseen circumstances, project managers should:
-
Assess the impact on capacity: When unforeseen circumstances arise, project managers should assess their impact on planned capacity. This involves evaluating the changes in resource availability, task dependencies, or project constraints and identifying any potential capacity constraints that may arise.
-
Take immediate actions: Once the impact of unforeseen circumstances on capacity is assessed, project managers should take immediate actions to adapt capacity plans. This may involve reallocating resources, adjusting project schedules, or seeking alternative solutions to mitigate the impact on capacity.
-
Communicate and collaborate: Effective communication and collaboration are crucial in managing capacity changes due to unforeseen circumstances. Project managers should engage with stakeholders, team members, and relevant parties to communicate changes, seek input, and collaboratively develop strategies to address the impact on capacity.
-
Learn from the experience: Unforeseen circumstances provide valuable learning opportunities. Project managers should conduct post-mortem reviews to evaluate the effectiveness of capacity management strategies and identify lessons learned. Applying these lessons to future projects helps in building resilience in capacity management and mitigating potential risks.
By actively managing capacity changes due to unforeseen circumstances and taking necessary actions to adapt capacity plans, project managers can minimize the impact on project outcomes and maintain project success.
Resilience in capacity management
Resilience is essential in capacity management to ensure projects can withstand unexpected challenges and disruptions. Building resilience involves embracing adaptability, proactively managing risks, and establishing robust contingency plans.
To foster resilience in capacity management, project managers should:
-
Develop a culture of adaptability: Project managers should promote a culture of adaptability within the project team. This involves encouraging individuals to be flexible, open to change, and proactive in identifying and addressing capacity constraints. By embracing adaptability, the team can respond effectively to unexpected challenges.
-
Continuously assess and manage risks: Identifying and managing risks should be an ongoing process throughout the project lifecycle. Project managers should regularly assess potential risks associated with capacity constraints, develop appropriate mitigation strategies, and continuously monitor and adjust these strategies as needed.
-
Establish robust contingency plans: Robust contingency plans are crucial in building resilience in capacity management. These plans should include backup resources, alternative approaches, and clear guidelines for adapting capacity plans in response to unexpected circumstances. By having these plans in place, project managers are better prepared to address capacity constraints and mitigate risks.
-
Encourage collaboration and knowledge sharing: By fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing within the project team, project managers can harness the collective expertise and skills to address capacity constraints. Encouraging team members to share lessons learned, best practices, and innovative ideas promotes resilience in capacity management.
By embracing resilience in capacity management, project managers can effectively respond to unexpected challenges, mitigate risks, and ensure the successful completion of projects.
Capacity Planning Tools and Techniques
Utilizing project management software for capacity planning
Project management software provides valuable tools for capacity planning. These software solutions offer features such as resource management, timeline visualization, and task allocation, facilitating effective capacity planning and resource utilization.
Key benefits of utilizing project management software for capacity planning include:
-
Resource visibility: Project management software provides visibility into resource availability, workload distribution, and task dependencies. This enables project managers to identify potential capacity constraints, allocate resources effectively, and optimize capacity utilization.
-
Real-time updates: Project management software allows for real-time updates on project progress, resource allocation, and task completion. This ensures that capacity plans are always up-to-date and reflect the current project status.
-
Forecasting and predictive analytics: Some project management software solutions offer forecasting capabilities and predictive analytics. These features allow project managers to anticipate resource needs, predict potential capacity constraints, and take proactive measures to address them.
-
Collaboration and communication: Project management software often includes collaboration tools and features that facilitate communication and collaboration among team members. This improves coordination, helps identify potential capacity constraints, and enables efficient capacity planning.
By utilizing project management software, project managers can streamline capacity planning processes, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall project efficiency.
Using resource management tools for capacity estimation
Resource management tools provide valuable assistance in capacity estimation. These tools help project managers assess resource availability, evaluate skill sets, and estimate resource utilization based on historical data or predefined parameters.
Key benefits of using resource management tools for capacity estimation include:
-
Resource evaluation: Resource management tools facilitate the evaluation of available resources, including their skill sets, expertise, and availability. By leveraging features such as resource profiles or skill matrices, project managers can accurately estimate the capacity of resources for specific tasks.
-
Historical data analysis: Resource management tools often include features for analyzing historical data related to resource utilization, task completion rates, or project outcomes. By leveraging this data, project managers can make more accurate capacity estimations based on past performance.
-
Scenario modeling: Resource management tools may offer scenario modeling capabilities that allow project managers to simulate different capacity scenarios based on various parameters. This enables project managers to assess the impact of different resource allocation strategies on overall capacity utilization.
-
Reporting and analytics: Resource management tools typically provide reporting and analytics features that allow project managers to generate insights into resource utilization, capacity forecasting, or potential constraints. These insights enable more informed decision-making during capacity planning.
By utilizing resource management tools, project managers can enhance their capacity estimation processes, improve accuracy, and make more data-driven decisions.
The role of technology in optimizing capacity planning
Technology plays a crucial role in optimizing capacity planning by providing tools and techniques that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration. The use of project management software, resource management tools, and other technological solutions enables project managers to overcome capacity constraints, make informed decisions, and maximize resource utilization.
Some key roles of technology in optimizing capacity planning include:
-
Automation: Technology enables the automation of various capacity planning tasks, reducing manual efforts and human errors. This includes automating resource allocation, task scheduling, or capacity forecasting, allowing project managers to focus on strategic decision-making.
-
Enhanced collaboration: Technology solutions facilitate communication, collaboration, and knowledge sharing within the project team. By leveraging features such as real-time updates, messaging platforms, or document sharing, project managers can foster a collaborative environment and optimize resource allocation.
-
Data-driven decision-making: Technology provides access to real-time data, metrics, and analytics that drive data-driven decision-making in capacity planning. By leveraging these insights, project managers can make informed decisions, identify potential capacity constraints, and optimize resource allocation.
-
Scalability and flexibility: Technology solutions are often scalable and adaptable, allowing for capacity planning that accommodates changing project requirements or constraints. This flexibility enables project managers to optimize capacity utilization despite evolving circumstances.
By embracing technology and leveraging the available tools and techniques, project managers can optimize capacity planning processes, enhance resource allocation, and ultimately improve project outcomes.
Capacity and Project Success
Achieving project goals through effective capacity management
Effective capacity management is a critical factor in achieving project goals. By understanding capacity requirements, properly allocating resources, and mitigating capacity constraints, project managers can optimize resource utilization, enhance efficiency, and increase the chances of project success.
Key benefits of effective capacity management in achieving project goals include:
-
Improved resource utilization: Effective capacity management ensures that resources are optimally allocated, minimizing underutilization or overloading. This leads to improved resource utilization and enhanced productivity, allowing project teams to achieve project goals more efficiently.
-
Mitigation of capacity constraints: Proper capacity management involves identifying and addressing potential capacity constraints early on. By mitigating these constraints, project managers can reduce the risk of delays, cost overrun, or compromised project outcomes, increasing the likelihood of achieving project goals.
-
Timely completion of tasks: Effective capacity management enables project managers to allocate resources appropriately and optimize task schedules. This helps in ensuring that tasks are completed in a timely manner, facilitating the achievement of project goals according to the planned timeline.
-
Quality deliverables: By effectively managing capacity, project managers can ensure that team members have the necessary time and resources to produce high-quality deliverables. This enhances the overall quality of project outcomes and increases the likelihood of meeting or exceeding stakeholder expectations.
By implementing effective capacity management practices, project managers can align resource allocation with project goals, optimize capacity utilization, and increase the chances of achieving project success.
Impact of capacity on project timeline and budget
Capacity directly impacts the project timeline and budget. Insufficient capacity can lead to delays, cost overrun, or compromised project outcomes, while effective capacity management ensures that projects stay on track and within budget.
The impact of capacity on project timeline and budget includes:
-
Delayed project timeline: Insufficient capacity or capacity constraints can lead to delays in project activities or milestones. If resources are not adequately allocated or if there are bottlenecks in resource utilization, tasks may take longer to complete, affecting the overall project timeline.
-
Increased project costs: Inefficient resource allocation or resource overloads resulting from capacity constraints can increase project costs. Additional resources may need to be recruited or outsourced, or tasks might need to be reassigned, leading to increased expenses.
-
Reduced productivity: Insufficient capacity or unbalanced workloads can significantly impact productivity. Overloaded team members may experience decreased performance, resulting in lower productivity levels. This can further impact the project timeline and budget.
-
Compromised project outcomes: When capacity is not effectively managed, there is a higher risk of compromised project outcomes. Insufficient resources, poor resource allocation, or capacity constraints can affect the quality of deliverables, leading to dissatisfied stakeholders or rework, further impacting the project budget.
By effectively managing capacity, project managers can optimize resource allocation, reduce the risk of delays or cost overrun, and ensure that projects stay on track within the planned timeline and budget.
Evaluating project success based on capacity utilization
Capacity utilization is an important measure in evaluating project success. It provides insights into how effectively resources have been utilized, tasks have been completed, and project goals have been achieved within the available capacity.
Key considerations in evaluating project success based on capacity utilization include:
-
Resource utilization rate: Assessing the resource utilization rate provides insights into how effectively resources have been allocated and utilized. A high resource utilization rate indicates efficient capacity management and a better chance of achieving project success.
-
Task completion rate: Evaluating the task completion rate helps in understanding the efficiency and progress of project activities. A high task completion rate indicates that tasks have been completed within the planned timeframe, enhancing project success.
-
Adherence to project schedule: Evaluating project schedule adherence is crucial in determining project success. If the project has been completed within the planned timeline or with minimal delays despite potential capacity constraints, it reflects successful capacity management.
-
Quality of project outcomes: The quality of project deliverables is a key indicator of project success. When capacity is effectively managed, team members have the necessary time and resources to produce high-quality deliverables, leading to enhanced project success.
By evaluating project success based on capacity utilization, project managers can assess the efficiency of capacity management efforts, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to optimize capacity utilization in future projects.
In conclusion, capacity in project management refers to the maximum amount of work that a team or organization can accomplish within a specific timeframe. Understanding and managing capacity is crucial in project management as it directly impacts the success of a project. Capacity planning involves understanding project requirements, identifying available resources, and estimating capacity for different project phases. Managing capacity constraints requires recognizing constraints, implementing strategies to alleviate them, and mitigating risks associated with capacity constraints. Optimizing capacity utilization involves maximizing efficiency through resource allocation, balancing workloads across the team, and optimizing capacity planning for multiple projects. Tracking and monitoring capacity involves implementing performance metrics, regularly reviewing and updating capacity plans, and fostering effective communication and collaboration. Capacity and risk management are closely related, and proactive capacity management helps in addressing risks associated with capacity constraints. Adapting capacity for changing situations requires flexibility, managing capacity changes due to unforeseen circumstances, and building resilience in capacity management. Capacity planning tools and techniques such as project management software and resource management tools play a vital role in optimizing capacity planning. Finally, capacity directly impacts project success by achieving project goals, influencing project timeline and budget, and evaluating project success based on capacity utilization.