In the world of project management, technical project management holds a vital role in ensuring the successful execution of complex projects. This article aims to provide you with a clear understanding of technical project management, its key components, and its significance in delivering projects on time and within budget. Whether you are a seasoned project manager or someone aspiring to take on this role, unpacking the nuances of technical project management will equip you with the knowledge and skills to thrive in this dynamic field. So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey together!
Understanding Technical Project Management
Definition of Technical Project Management
Technical project management refers to the practice of planning, organizing, and executing projects in the field of technology. It involves overseeing the development and implementation of technical solutions to meet specific objectives and deliverables. Technical project managers are responsible for ensuring that projects are completed on time, within budget, and according to the defined scope. They play a crucial role in coordinating teams, allocating resources, managing risks, and communicating with stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle.
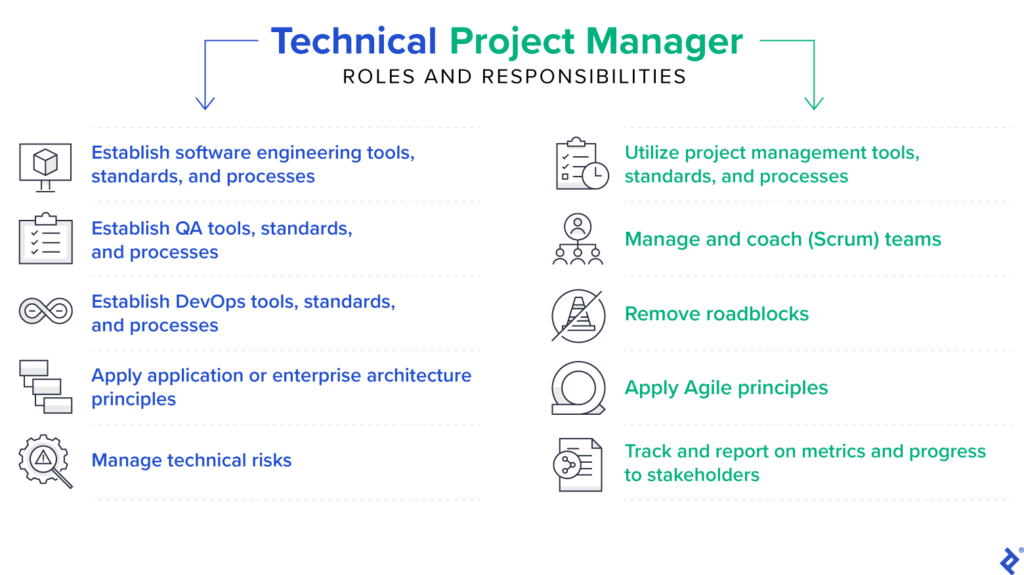
Role and Responsibilities of a Technical Project Manager
As a technical project manager, your primary role is to lead the successful delivery of technical projects. This involves a range of responsibilities, including:
-
Project Planning: You are responsible for creating a project plan and timeline, defining project goals and objectives, and establishing the scope and deliverables. This requires a thorough understanding of the project requirements, technology, and available resources.
-
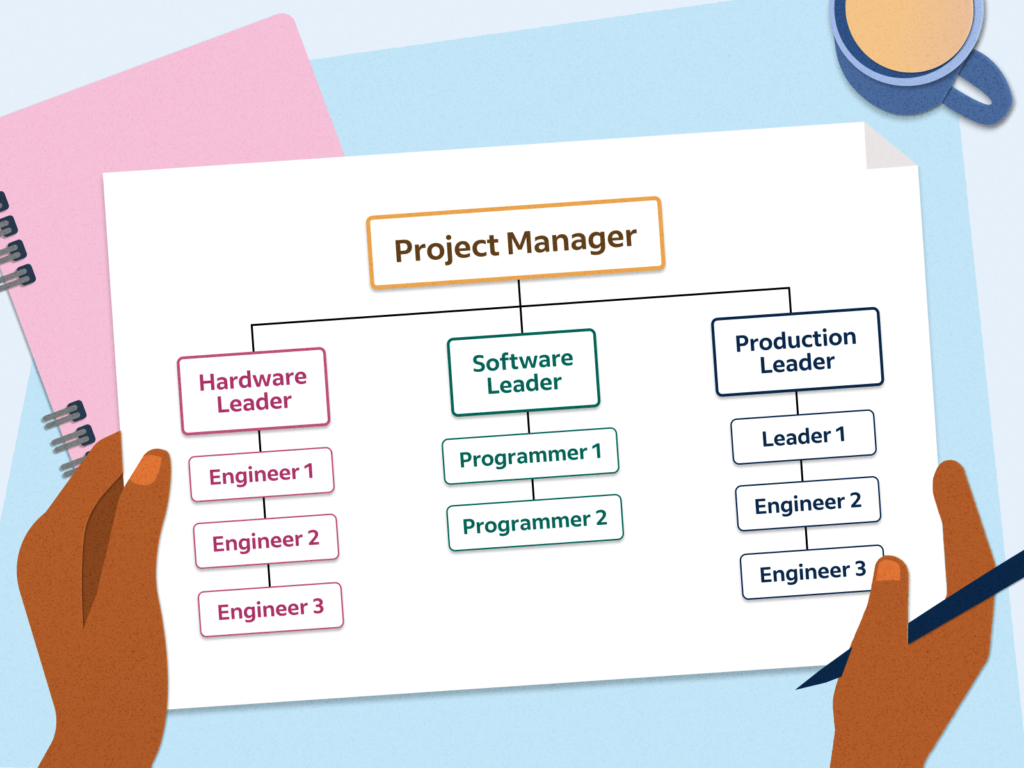
Team Management: You are responsible for building and motivating a technical project team, delegating tasks and responsibilities, and providing support and mentorship to team members. Effective team management is vital to ensure that each team member’s skills and expertise are utilized to their fullest potential.
-
Risk Management: It is your responsibility to identify and assess project risks, develop mitigation strategies, and monitor and control risks throughout the project lifecycle. This includes identifying potential technical issues and taking proactive measures to address them.
-
Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration are key to successful project management. You must establish clear communication channels, facilitate regular progress reporting, and manage stakeholder expectations. Additionally, you must foster a collaborative environment that encourages open communication and knowledge sharing among team members.
-
Quality Assurance and Testing: Ensuring the quality of deliverables is another crucial responsibility. You are responsible for developing and implementing quality standards, conducting testing and quality control activities, and ensuring complete and accurate documentation.
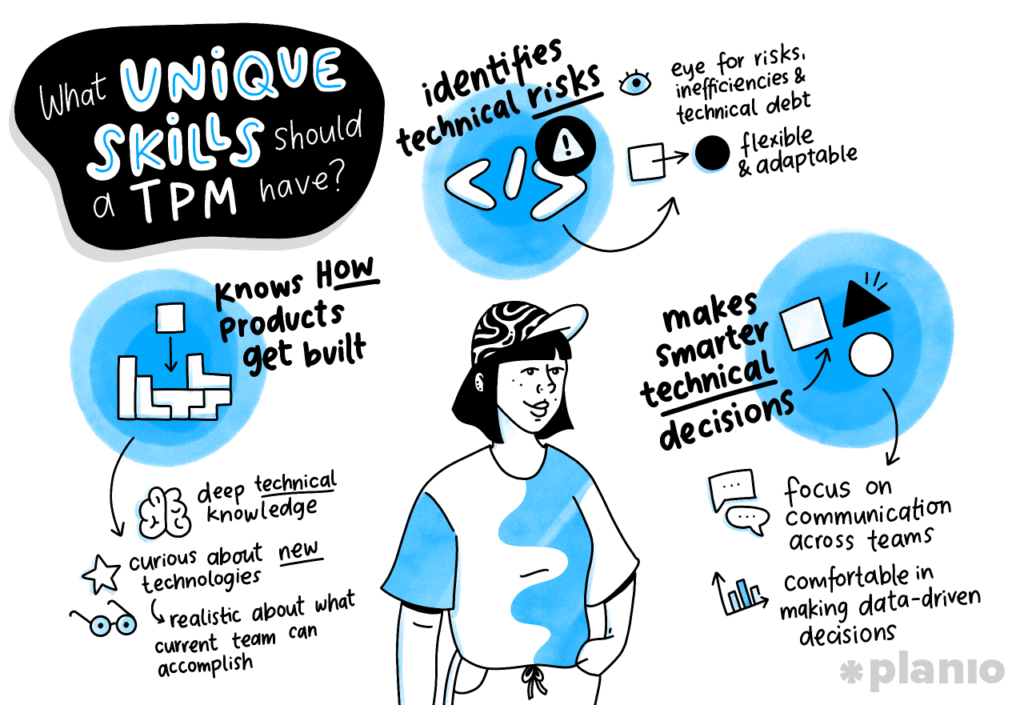
Key Skills and Qualifications for Technical Project Managers
To excel in technical project management, certain key skills and qualifications are essential. These include:
-
Technical Expertise: A strong technical background is vital to understanding the complexities and requirements of the projects you will be managing. This includes knowledge of relevant technologies, tools, and industry best practices.
-
Project Management Knowledge: A solid understanding of project management methodologies, frameworks, and practices is necessary to effectively plan, execute, and monitor projects. This includes knowledge of project management software and tools.
-
Leadership and Communication Skills: As a technical project manager, you must be a strong leader and an effective communicator. You should possess the ability to motivate and inspire your team, resolve conflicts, and communicate with stakeholders at all levels.
-
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making Abilities: Technical projects often encounter challenges and obstacles that require quick thinking and decisive action. A project manager should possess strong problem-solving and decision-making skills to overcome these hurdles and keep the project on track.
-
Organizational and Time Management Skills: The ability to prioritize tasks, manage resources effectively, and meet deadlines is crucial for successful project management. Strong organizational and time management skills are essential to keep projects on schedule and within budget.
Project Initiation
Defining Project Goals and Objectives
In the project initiation phase, it is crucial to clearly define the goals and objectives of the project. This involves understanding the client or organization’s requirements and expectations and translating them into specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) project objectives. The project goals should align with the overall strategic objectives and vision of the organization.
Identifying Stakeholders and Creating a Project Team
Identifying and engaging stakeholders is an essential step in project initiation. Stakeholders are individuals or groups who have an interest or involvement in the project and can significantly impact its success. It is important to identify key stakeholders and understand their expectations and requirements. Once stakeholders are identified, a project team can be created, consisting of individuals with the necessary skills and expertise to contribute to the project’s success.
Establishing Scope and Deliverables
Establishing the project scope involves clearly defining the boundaries of the project and determining what will be included and excluded. It is essential to document the scope statement, which outlines the project’s deliverables, constraints, assumptions, and any exclusions. Clearly defining the scope helps prevent scope creep and ensures that the project stays on track.
Project Planning
Creating a Project Plan and Timeline
Creating a comprehensive project plan is a critical aspect of project management. The project plan serves as a roadmap, outlining the tasks, milestones, and activities required to complete the project. It should include a detailed timeline, identifying dependencies and sequencing of tasks. The project plan should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure its accuracy and effectiveness.
Allocating Resources and Budgeting
Resource allocation involves assigning the right people with the appropriate skills and expertise to specific project tasks. It also includes allocating equipment, facilities, and other resources required for the project’s successful execution. Additionally, budgeting involves estimating and allocating financial resources to cover project expenses, ensuring that the project remains within the approved budget.
Identifying Project Risks and Developing Mitigation Strategies
Identifying and assessing project risks is a critical step in project planning. Risk identification involves identifying potential threats and opportunities that may impact the project’s success. Once risks are identified, mitigation strategies can be developed to minimize the impacts of potential threats and capitalize on opportunities. Regular monitoring and controlling of risks throughout the project lifecycle are necessary to ensure project success.
Managing Project Execution
Effective Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are essential throughout the project execution phase. This includes regularly communicating project updates, changes, and milestones to all stakeholders. Collaborating with team members and stakeholders fosters a positive and productive working environment and ensures that everyone is aligned and working towards the project’s goals.
Tracking Progress and Managing Changes
Tracking project progress involves monitoring the completion of tasks, milestones, and deliverables against the planned schedule. This helps identify any deviations from the project plan and enables timely corrective actions to be taken. Additionally, managing changes includes evaluating and implementing change requests, assessing their impacts on the project, and ensuring that changes align with the project’s objectives.
Managing and Resolving Technical Issues
Technical projects often encounter technical issues and challenges that require prompt resolution. It is the project manager’s responsibility to identify and address these issues, ensuring that they do not hinder project progress. This involves collaborating with technical experts, analyzing the issues, and implementing appropriate solutions to minimize disruptions and keep the project on track.
Team Leadership and Management
Building and Motivating a Technical Project Team
Building a high-performing project team is crucial for project success. This involves selecting individuals with the relevant skills and expertise for each project role and ensuring that the team members have a clear understanding of their responsibilities. Motivating the team involves fostering a positive work environment, recognizing achievements, and providing support and guidance when needed.
Delegating Tasks and Responsibilities
Delegating tasks and responsibilities is an essential skill for a project manager. It involves assigning tasks to team members based on their skills and expertise, providing clear instructions and expectations, and empowering them to take ownership and accountability for their assigned tasks. Effective delegation not only ensures the timely completion of tasks but also fosters professional growth and development within the team.
Providing Support and Mentorship
As a project manager, it is important to provide support and mentorship to team members throughout the project lifecycle. This includes facilitating training and development opportunities, providing guidance and feedback, and helping team members overcome challenges. By actively supporting and mentoring the team, you create a positive and collaborative environment that promotes continuous learning and growth.
Quality Assurance and Testing
Developing and Implementing Quality Standards
Developing and implementing quality standards ensures that project deliverables meet the required quality expectations. This involves establishing quality assurance processes, defining quality metrics and benchmarks, and integrating quality checks throughout the project lifecycle. Adhering to quality standards helps prevent errors and defects and ensures the successful delivery of a high-quality project.
Conducting Testing and Quality Control
Testing and quality control activities are crucial for identifying and addressing any defects or issues in project deliverables. This includes conducting various types of testing, such as functional testing, performance testing, and user acceptance testing. The results of testing are closely monitored, and any identified issues are resolved before the final delivery of the project.
Ensuring Complete and Accurate Documentation
Complete and accurate documentation is essential for project success and future reference. This includes documenting project requirements, design specifications, test plans, and user manuals. Thorough documentation enables effective knowledge transfer, facilitates troubleshooting, and ensures that project deliverables can be maintained and enhanced in the future.
Project Communication and Reporting
Establishing Communication Channels
Establishing effective communication channels is crucial for project success. This involves determining the appropriate communication methods, tools, and frequency to engage with stakeholders and team members. Clear and open communication channels foster collaboration, resolve issues promptly, and keep stakeholders informed of project progress.
Regular Progress Reporting
Regular progress reporting is important to keep stakeholders informed about the project’s status. This includes providing updates on completed tasks, milestones achieved, and any changes or challenges encountered. Progress reports should be concise, informative, and tailored to the needs of each stakeholder, ensuring that they have the necessary information to make informed decisions and support the project.
Managing Stakeholder Expectations
Managing stakeholder expectations is a critical aspect of project management. It involves understanding the needs and requirements of stakeholders, communicating project progress and changes effectively, and addressing any concerns or issues promptly. Managing stakeholder expectations helps build trust and maintain positive relationships, ensuring their continued support throughout the project.
Risk Management
Identifying and Assessing Project Risks
Identifying and assessing project risks is a continuous process throughout the project lifecycle. This involves actively identifying potential risks, such as technical challenges, resource constraints, or external dependencies, and assessing their likelihood and potential impacts on the project. Risk identification and assessment enable proactive planning and implementation of mitigation strategies.
Developing Risk Mitigation Strategies
After identifying and assessing project risks, appropriate risk mitigation strategies should be developed. These strategies aim to minimize the likelihood or impact of potential risks. Mitigation strategies may include alternative approaches, contingency plans, or preventive measures. Regular monitoring and controlling of risks are necessary to ensure that the mitigation strategies remain effective throughout the project.
Monitoring and Controlling Risks
Monitoring and controlling risks is an ongoing process in technical project management. This involves regularly reviewing and reassessing identified risks, monitoring the effectiveness of implemented mitigation strategies, and taking corrective actions as necessary. Effective risk management ensures that project risks are managed proactively and that potential impacts are minimized.
Project Closure
Conducting Project Evaluation and Lessons Learned
Project closure involves conducting a comprehensive evaluation of the project’s performance and outcomes. This includes assessing whether the project goals and objectives were achieved, evaluating project deliverables against the defined specifications, and analyzing the project’s overall success. Lessons learned from the project are then identified, documented, and shared, allowing for continuous improvement in future projects.
Documenting Project Success and Achievements
Documenting project success and achievements is an important step in project closure. This includes capturing key project metrics, such as on-time delivery, adherence to budget, and customer satisfaction. Additionally, showcasing successful project outcomes and the value delivered to stakeholders helps build a positive reputation for the project manager and the project team.
Transferring Knowledge and Deliverables
Transferring knowledge and deliverables to relevant stakeholders is essential for a smooth project closure. This involves documenting and organizing project-related information, ensuring that project documentation and deliverables are easily accessible, and facilitating knowledge transfer sessions with the appropriate parties. Transfer of knowledge and deliverables enables stakeholders to understand and utilize the project outcomes effectively.
Tools and Technologies for Technical Project Management
Project Management Software
Project management software plays a crucial role in technical project management. These tools help streamline project planning, execution, and monitoring by providing features such as task management, scheduling, resource allocation, and progress tracking. Popular project management software includes Microsoft Project, Jira, and Asana.
Collaboration Tools
Collaboration tools enable effective communication and collaboration among team members and stakeholders. These tools facilitate real-time communication, document sharing, and task collaboration, allowing team members to work together regardless of their geographical location. Examples of collaboration tools include Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Google Drive.
Task and Time Tracking Tools
Task and time tracking tools help project managers and team members monitor and record the time spent on various project tasks. These tools assist in tracking project progress, identifying potential bottlenecks, and estimating resource requirements for future projects. Examples of task and time tracking tools include Toggl, Harvest, and Clockify.
In conclusion, technical project management encompasses various roles, responsibilities, and skills that are essential for successfully managing and delivering technical projects. From project initiation to closure, effective planning, communication, team management, risk mitigation, and quality assurance are key aspects of technical project management. By utilizing appropriate tools and technologies, project managers can streamline project processes and ensure the successful delivery of projects within the defined scope, timeline, and budget.