Ever wondered how to effectively manage projects in a fast-paced and constantly evolving environment? Look no further than the agile project management methodology. Agile project management is a flexible and iterative approach that emphasizes collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement. By breaking down complex projects into manageable tasks and fostering open communication within teams, agile project management allows for quick adjustments and better outcomes. Sounds intriguing, doesn’t it? Let’s explore more about this dynamic methodology to gain a deeper understanding of its benefits and how it can positively impact your project management endeavors.
Understanding Agile Project Management Methodology
Agile project management methodology has become increasingly popular in recent years, as organizations seek more flexible and adaptive approaches to project execution. This methodology is widely regarded as a game-changer in the project management world, revolutionizing the way teams work and deliver projects. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of Agile project management, including its definition, key principles, benefits, team roles, frameworks, methodologies, tools, implementation, challenges, and success stories. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will have a solid understanding of Agile project management methodology and its potential to transform your project’s success.
What is Agile Project Management?
Definition of Agile Project Management
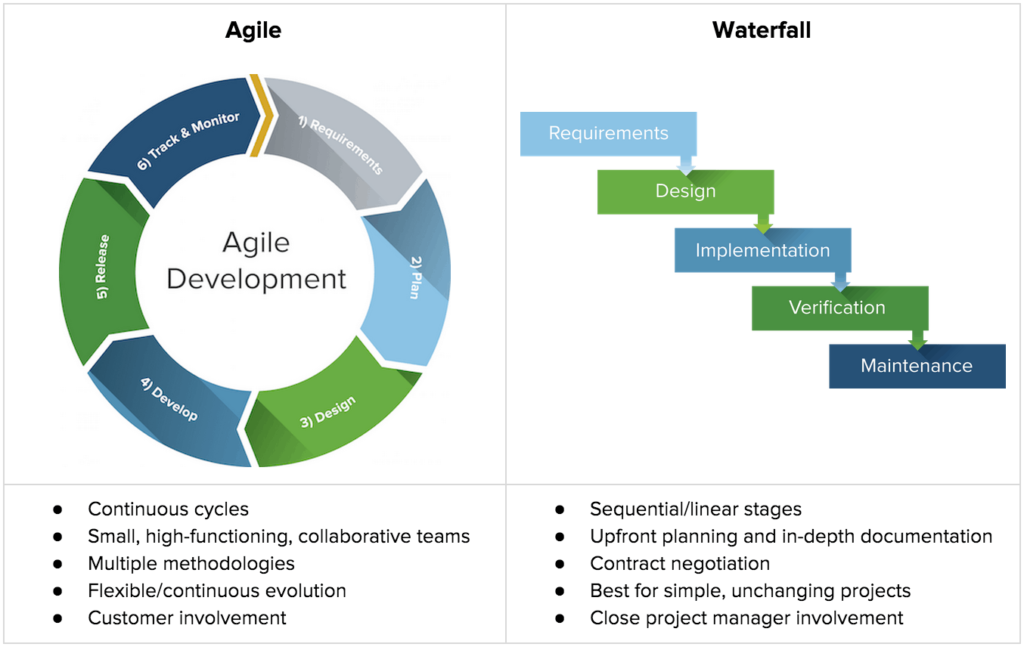
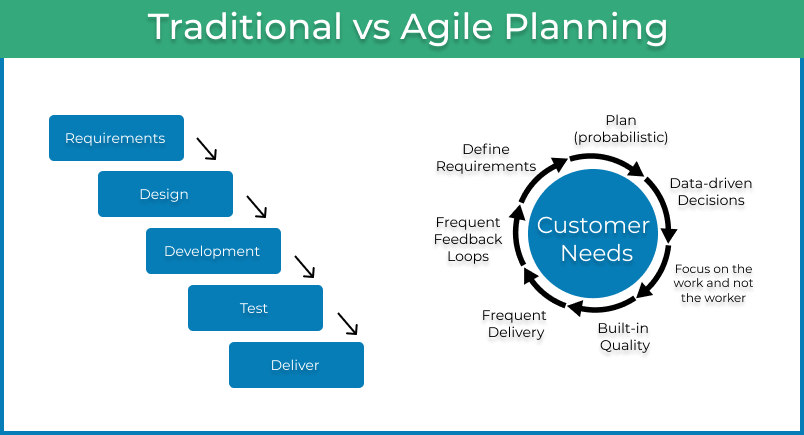
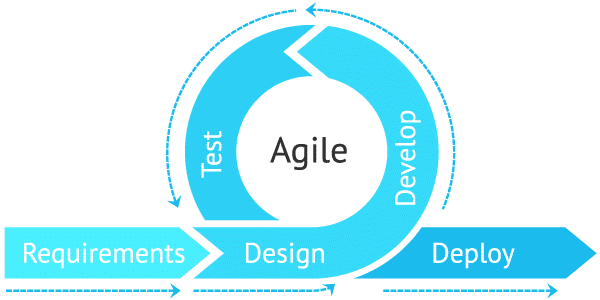
Agile project management is an iterative and flexible approach to project execution that prioritizes customer satisfaction and continuously adapts to changing requirements. Unlike traditional project management methodologies that rely on rigid plans and deliverables, Agile focuses on collaborative and incremental development, allowing teams to respond quickly to evolving customer needs and market dynamics.
Key Principles of Agile Project Management
Agile project management is guided by a set of key principles that drive its success:
-
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation: Agile projects prioritize direct and continuous customer involvement to ensure that the deliverables meet their expectations and provide maximum value.
-
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools: Agile methodologies emphasize the importance of effective communication and collaboration among team members, valuing their expertise and focusing on continuous improvement.
-
Working solutions over comprehensive documentation: Instead of extensive documentation, Agile projects prioritize delivering tangible and valuable solutions that can be rapidly tested and refined based on customer feedback.
-
Responding to change over following a plan: Agile embraces change as a natural part of the project lifecycle and encourages teams to be flexible and adaptable, adjusting their course of action based on new insights and emerging requirements.
Benefits of Agile Project Management
Agile project management offers numerous benefits that make it an attractive choice for modern organizations. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
Increased Flexibility and Adaptability
Agile methodologies provide the flexibility to accommodate changing requirements and priorities throughout the project. By embracing iterative development and continuous feedback, teams can respond swiftly to market shifts, technological advancements, and customer demands. This adaptability ultimately leads to better outcomes and higher customer satisfaction.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Agile project management methodologies foster an environment of collaboration and communication. By emphasizing frequent interaction between team members, stakeholders, and customers, Agile ensures that everyone is aligned and working towards a common goal. This increased collaboration improves relationships, reduces misunderstandings, and encourages knowledge sharing, leading to more efficient and effective project delivery.
Faster Delivery of Value
One of the primary goals of Agile is to deliver value to the customer as quickly as possible. By breaking down projects into smaller, manageable increments called iterations or sprints, Agile teams can prioritize and deliver the most valuable features or functionalities first. This iterative approach allows for earlier delivery and feedback, enabling teams to address any issues or make improvements sooner.
Improved Quality and Customer Satisfaction
Agile methodologies focus on delivering working solutions throughout the project’s lifecycle, fostering a spirit of continuous improvement. By regularly testing and refining deliverables based on customer feedback, Agile teams can ensure that the final product meets or exceeds expectations. This emphasis on quality and customer satisfaction ultimately leads to higher levels of customer loyalty and positive brand reputation.
Agile Project Team Roles
In Agile project management, there are three primary roles that contribute to the success of a project:
Product Owner
The Product Owner is responsible for representing the customer or end-user throughout the project. Their role involves defining and prioritizing the project’s requirements and ensuring that the delivered product aligns with the customer’s vision. They work closely with the Agile team, providing clarifications, guidance, and feedback when necessary.
Scrum Master
The Scrum Master is the team’s facilitator and coach, guiding the team in using and adhering to Agile principles and the chosen framework. They remove obstacles that hinder the team’s progress, facilitate communication and collaboration, and ensure that the Agile rituals (such as daily stand-up meetings) are effectively executed. The Scrum Master serves as the advocate for the team, protecting them from external distractions and ensuring a conducive work environment.
Development Team
The Development Team consists of the individuals responsible for executing the project. They collectively possess the necessary skills and expertise to deliver the project’s requirements. The Development Team collaboratively works on the deliverables, continuously adapting and improving their processes to achieve higher productivity and quality. They are self-organizing and cross-functional, actively participating in all aspects of the project’s development.
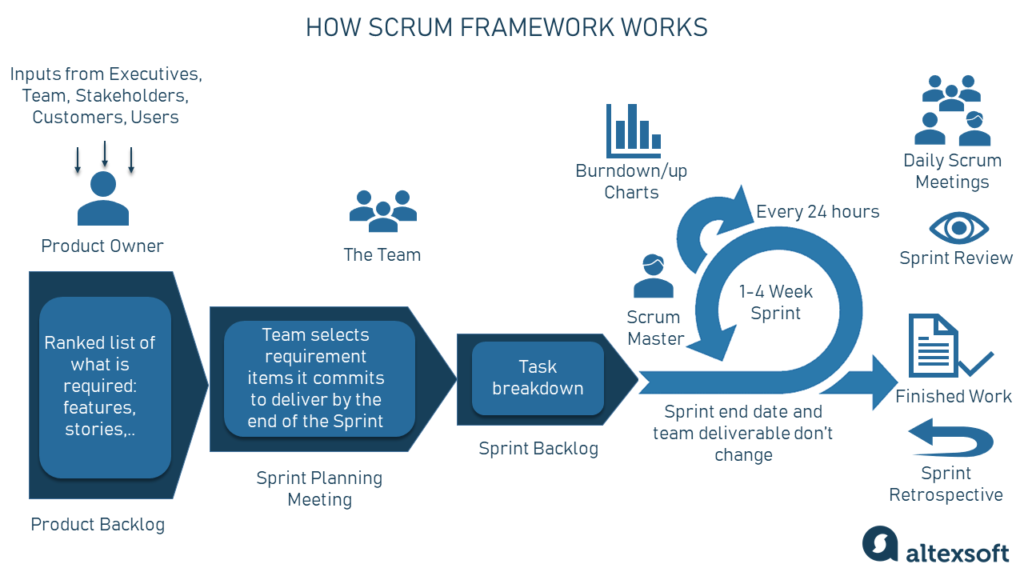
Scrum Framework
Scrum is one of the most widely used frameworks within Agile project management. It provides a structured approach for delivering complex work through iterative and incremental development. Let’s explore the key components of the Scrum framework:
Sprints
Sprints are time-boxed periods (typically two to four weeks in length) during which the Development Team works on delivering a set of prioritized requirements. The goal of each sprint is to produce a potentially shippable increment of deliverables that align with the project’s objectives.
Product Backlog
The Product Backlog is a dynamic list of all the requirements or features that need to be implemented in the project. It serves as the single source of truth for the Development Team, Product Owner, and Scrum Master. The Product Backlog is continuously refined and reprioritized based on customer feedback, market changes, and emerging requirements.
Sprint Planning
Sprint Planning is a collaborative session that occurs at the beginning of each sprint. The Development Team and Product Owner work together to decide which requirements to include in the upcoming sprint, considering their priority and capacity. The expected outcome of Sprint Planning is a well-defined Sprint Goal and a clear plan for how the selected requirements will be implemented.
Daily Stand-up Meetings
Daily Stand-up Meetings, also known as Daily Scrums, are short, time-boxed meetings that occur every day during a sprint. Its purpose is to update the entire team on individual progress, synchronize activities, and identify any potential issues or roadblocks. This brief daily check-in promotes transparency, accountability, and collaboration among team members.
Sprint Review
The Sprint Review is held at the end of each sprint to showcase the work completed during the iteration. The Development Team presents the potentially shippable increment to the Product Owner, stakeholders, and other relevant parties. This feedback session allows for validation of the deliverables and review of any changes or adjustments needed.
Sprint Retrospective
The Sprint Retrospective is a reflective session held after the Sprint Review, allowing the team to analyze and improve their processes. It provides an opportunity to identify potential areas of improvement, discuss what worked well and what didn’t, and define actions to enhance future sprints. The Sprint Retrospective ensures that the team continuously learns and grows as they progress through the project.
Other Agile Methodologies
While Scrum is a popular Agile framework, there are several other methodologies that organizations can choose from based on their needs and preferences. Some of these methodologies include:
Kanban
Kanban is a visual project management framework that focuses on the flow and efficiency of work. It is based on the concept of a Kanban board, which visually represents the project’s tasks or work items at different stages of completion. Kanban emphasizes limiting work in progress, promoting continuous delivery, and optimizing workflow.
Lean
Lean is a methodology that originated from manufacturing and has since been applied to project management. Lean aims to eliminate waste, minimize bottlenecks, and improve overall efficiency. By identifying and optimizing processes, Lean helps organizations streamline their operations and deliver value more effectively.
Extreme Programming (XP)
Extreme Programming (XP) is an Agile methodology that emphasizes close collaboration between developers and customers. It emphasizes an incremental and iterative approach to software development, with an emphasis on continuous integration, rapid feedback loops, and well-defined coding practices. XP aims to deliver high-quality software in shorter cycles.
Common Agile Project Management Tools
To support the successful implementation of Agile project management, numerous tools and software have been developed. These tools help teams manage and visualize project progress, facilitate collaboration, and track deliverables. Here are some commonly used Agile project management tools:
Jira
Jira is a versatile project management tool that offers a wide range of features to support Agile workflows. It allows teams to create and manage tasks, track progress using customizable boards, and generate reports on project metrics. Jira integrates with various other tools, enabling seamless collaboration across teams and departments.
Trello
Trello is a simple and intuitive project management tool that uses boards, lists, and cards to facilitate project tracking and collaboration. It provides a visual overview of tasks, allowing teams to manage their workflows efficiently. Trello’s simplicity and user-friendly interface make it a popular choice for small to medium-sized Agile teams.
Asana
Asana is a comprehensive project management tool that supports Agile methodologies and offers features to manage tasks, deadlines, and communication effectively. It allows teams to visualize projects through boards, track progress, and collaborate seamlessly. Asana also integrates with a wide range of other tools, enhancing productivity and coordination.
Implementing Agile Project Management
Implementing Agile project management requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some key steps to follow:
Defining project goals and scope
Before embarking on an Agile project, clearly define the project’s goals, objectives, and scope. This initial stage helps set expectations and creates a foundation for effective planning and execution.
Creating user stories and prioritizing backlog
User stories are short, simple descriptions of a specific feature or functionality from the user’s perspective. They serve as the building blocks for Agile projects. Collaborate with stakeholders and the Development Team to create user stories and prioritize them in the Product Backlog.
Iterations and sprint planning
Break down the project into smaller iterations or sprints. Collaborate with the Development Team and Product Owner to select relevant user stories for each sprint, considering overall project goals, available resources, and team capacity.
Tracking progress and adjusting
Regularly track the progress of the project through visualizations such as Kanban boards or Agile project management tools. Monitor key metrics, such as velocity and burn-down charts, to gain insights into team performance and adapt the project plan as needed.
Continuous improvement
Embrace a culture of continuous improvement throughout the project. Encourage team members to share their ideas, feedback, and learnings during Sprint Retrospectives. Continuously refine processes, optimize workflows, and seek opportunities for enhancing efficiency and effectiveness.
Challenges of Agile Project Management
While Agile project management offers numerous benefits, it also presents some unique challenges that organizations should be aware of:
Resistance to Change
Implementing Agile methodologies may face resistance from team members or stakeholders accustomed to more traditional approaches. The shift towards a more flexible, adaptive, and iterative approach can require a change in mindset and working practices.
Scope Creep
Without proper discipline and stakeholder management, Agile projects may be susceptible to scope creep – the continuous expansion of requirements or functionalities beyond the original project scope. It is essential to set clear boundaries and manage expectations to prevent scope creep from derailing the project.
Lack of Experience or Knowledge
Adopting Agile methodologies successfully requires a solid understanding of Agile principles, frameworks, and practices. Lack of experience or knowledge among team members can hinder the effective implementation of Agile project management, leading to suboptimal results.
Team Dynamics
Successful Agile project management depends on effective collaboration and communication within the team. If team dynamics are not well-managed, conflicts or communication breakdowns might hamper productivity and the overall success of the project.
Success Stories of Agile Project Management
Numerous organizations have achieved significant success by adopting Agile project management methodologies. For example, Spotify, the popular music streaming platform, attributes its rapid growth and continuous innovation to Agile practices. By embracing cross-functional teams, streamlined workflows, and iterative development, Spotify has been able to adapt to market changes and consistently deliver valuable features and enhancements.
Another notable success story is Scrum adoption at Lockheed Martin. The aerospace company utilized Agile project management to develop the F-35 fighter jet, one of the world’s largest defense projects. Agile methodologies helped Lockheed Martin streamline their development process, improve communication, and deliver a high-quality product on time and within budget.
Conclusion
Agile project management methodology has undoubtedly reshaped the way projects are executed, promoting flexibility, collaboration, and customer-centricity. By embracing Agile, organizations can increase their adaptability, enhance team collaboration, deliver value faster, and ultimately achieve higher levels of customer satisfaction. While challenges may arise, the benefits of Agile project management make it an invaluable tool for navigating the complexities of the modern business world. With a solid understanding of Agile principles, methodologies, and tools, you are well-equipped to embark on your Agile project management journey and unlock its transformative potential.